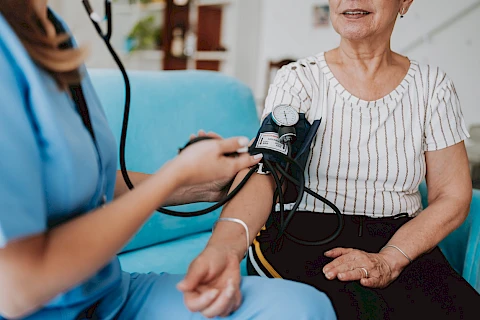
Monitoring seniors’ blood pressure is crucial for maintaining their health and well-being. As a caregiver, you are important in managing seniors' health and helping them live comfortably and safely. Senior Helpers will empower caregivers with essential knowledge about senior blood pressure readings and offer practical advice on monitoring and recording them effectively.
Blood Pressure Basics
Blood pressure measures the force of blood against the walls of the arteries. It has two components: systolic and diastolic pressure. Systolic pressure, the higher value, shows the pressure when the heart beats. Diastolic pressure, on the other hand, is the lower value and shows the pressure when the heart is at rest between beats.
A normal blood pressure range for seniors is generally around 120/80 mmHg, though this can vary. Remember that age, medication, and overall health influence senior blood pressure.
Proper Technique for Measuring Senior Blood Pressure
To obtain accurate blood pressure readings, follow these steps:
- Choose a well-fitting cuff, which can be manual or automatic.
- Have the senior sit comfortably with their back supported, feet flat on the floor, and arms supported at heart level.
- Ensure they are relaxed. Avoid measuring immediately after eating, drinking caffeine, or exercising.
- Place the cuff on the senior’s bare upper arm. If you are using an automatic monitor, you can follow the instructions on the screen.
- Take readings at the same time each day for consistency.
Proper equipment and techniques ensure reliability. Although automatic monitors are often preferred for their ease of use, manual monitors can be more accurate when used correctly.
Recording and Tracking Senior Blood Pressure Readings
Keeping a log of senior blood pressure readings helps track changes over time. Record the date, time, and reading each time you measure. This helps identify patterns or triggers that affect blood pressure. Various tools and apps can assist in recording and analyzing blood pressure data, making tracking more manageable and accessible.
When to Be Concerned: Recognizing Abnormal Readings
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a reading above 140/90 mmHg. Low blood pressure, or hypotension, can be below 90/60 mmHg. Both conditions can be concerning, especially if accompanied by dizziness, headache, or chest pain. If these symptoms occur or seniors’ blood pressure readings remain outside the normal range, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Empowering Caregivers With Knowledge
Staying informed and proactive is key to being an effective caregiver. Take advantage of resources and educational materials that deepen your understanding of senior health. Don't hesitate to ask questions or seek clarification from healthcare providers. By empowering yourself with knowledge, you contribute significantly to the well-being of the seniors in your care.
Discover Comprehensive Senior Services From Senior Helpers
We've covered the basics of understanding senior blood pressure, how to measure and record it accurately, and when to be concerned about abnormal readings. By staying informed and vigilant, caregivers can positively impact seniors’ health. For more support and resources, click here to find a Senior Helpers location near you!

